光学遥感图像目标检测算法综述(三)
原文pdf下载:下载链接
4. 数据集和算法性能比较
4.1 遥感图像目标检测数据集
常见数据集
| 论文 | 数据集名称 |
|---|---|
| [127]Heitz G, Koller D. Learning spatial Context: Using stuff to find things. In: Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2008). Marseille, France: Springer, 2008. 30−43 | TAS 数据集 |
| [128]Maggiori E, Tarabalka Y, Charpiat G, Alliez P. Can semantic labeling methods generalize to any city? The inria aerial image labeling benchmark. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Interna- tional Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). Fort Worth, USA: IEEE, 2017. 3226−3229 | SZTAKI-INRIA 数据集 |
| [129]Cheng G, Han J W, Zhou P C, Guo L. Multi-class geospatial object detection and geographic image classification based on collection of part detectors. ISPRS Journal of Photogram- metry and Remote Sensing, 2014, 98: 119−132 | NWPU VHR-10 数据集 |
| [130]Razakarivony S, Jurie F. Vehicle detection in aerial imagery: A small target detection benchmark. Journal of Visual Commu- nication and Image Representation, 2016, 34: 187−203 | VEDAI 数据集 |
| [131]Zhu H G, Chen X G, Dai W Q, Fu K, Ye Q X, Jiao J B. Ori- entation robust object detection in aerial images using deep convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Quebec City, Canada: IEEE, 2015. 3735−3739 | UCAS-AOD 数据集 |
| [132]Liu K, Mattyus G. Fast multiclass vehicle detection on aerial images. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(9): 1938−1942 | DLR 3K Vehicle 数据集 |
| [133]Liu Z K, Yuan L, Weng L B, Yang Y P. A high resolution op- tical satellite image dataset for ship recognition and some new baselines. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2017). Porto, Portugal: SciTe Press, 2017. 324−331 | HRSC2016 数据集 |
| [79]Long Y, Gong Y P, Xiao Z F, Liu Q. Accurate object localiza- tion in remote sensing images based on convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sens- ing, 2017, 55(5): 2486−2498 | RSOD 数据集 |
| [119]XiaGS,BaiX,DingJ,ZhuZ,BelongieS,LuoJB,etal. DOTA: A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial im- ages. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3974−3983 | DOTA 数据集 |
| [4]Li K, Wan G, Cheng G, Meng L Q, Han J W. Object detec- tion in optical remote sensing images: A survey and a new benchmark. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 159: 296−307 | DIOR 数据集 |
4.2 通用目标检测算法性能比较
评价因素
精确度 (Precision):被检测出来的目标中, 检测正确的概率。
召回率 (Recall):映所有待检测目标中被成功检测到的概率。
精度−召回率曲线(PR曲线):以召回率为横坐标、精确度为纵坐标画出的曲线。
平均精度(AP):PR曲线下对应的面积,单一类别的检测性能。
平均 AP 值(mAP):所有类别的平均 AP 值。
NWPU VHR-10 :类别数较少, 任务相对简单, 是早期深度学习算法广泛使用的数据集;
DOTA :数据集更加复杂, 检测难度更大, 是现阶段的主要评测数据集
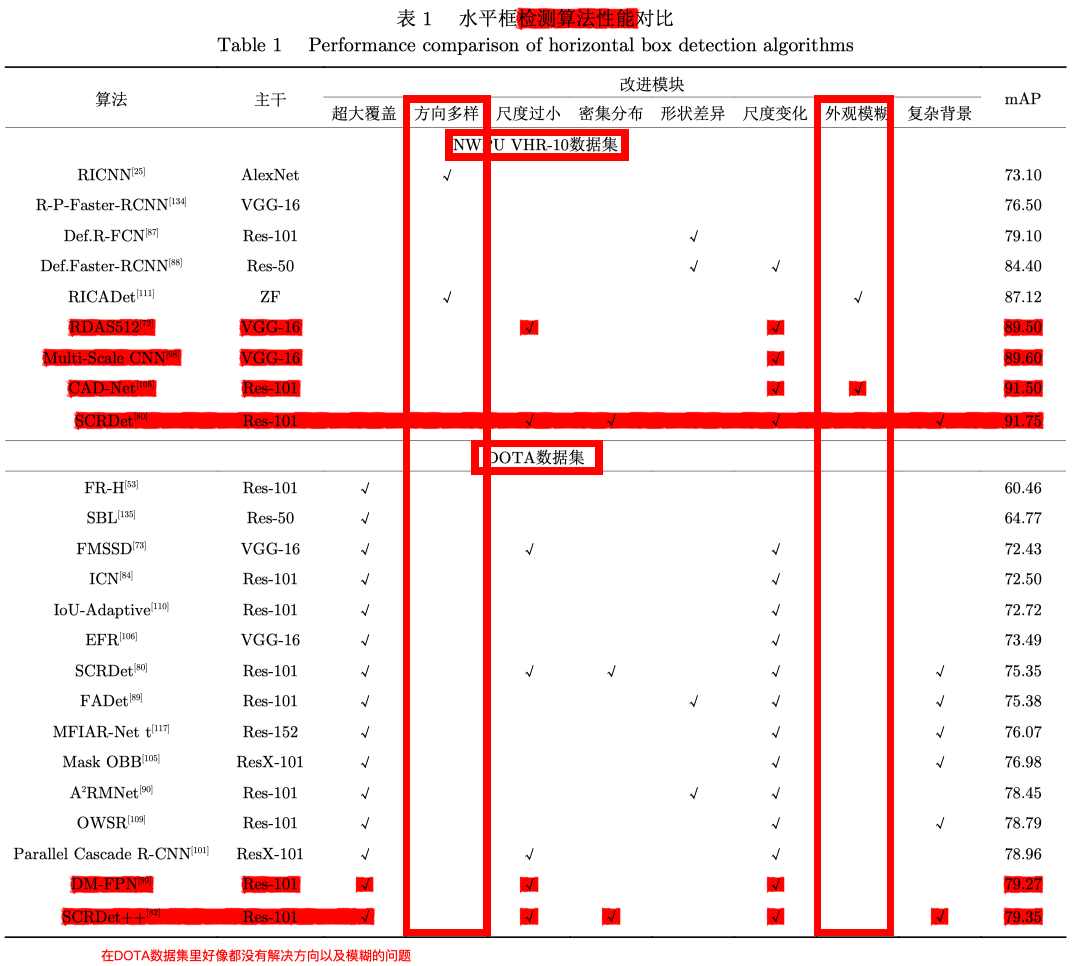
表格得到的信息:
(1)在处理更复杂和更有挑战性的问题时,很多问题目前还无法得到有效解决, 现有研究成果还无 法满足高标准应用场合需求。
(2)针对遥感图像目标自身特点进行的一系列改进是有效的。
(3)鉴于旋转框对目标的定位更加精细,旋转框检测在遥感领域应用潜力不断提高,旋转框检测的 mAP 值要略低于水平框(因为更严格),难度更高。
(4)遥感图像目标检测性能提升很大程度依赖深度学习自身的发展。
(5)图像分块的方式已经成为 DOTA 上公认的标准预处理方式。
(6)多尺度特征金字塔进行检测的方式, 可以有效处理目标尺度范围变化大的问题。
(7)现有针对密集分布、外观模糊的目标检测研究成果并不多。
5. 现存问题和发展趋势
5.1 现存问题
(1) 针对超大图像尺寸的遥感图像目标检测, 现有方法尚不能直接对图像全局进行检测(分块效率低,计算冗余)。
(2)针对遥感图像中目标密集分布和外观模糊等常见特点, 目前还没有较好的针对性处理方式。
(3)现有目标检测方法大多是基于目标本身视觉特征, 缺少根据图像整体和上下文进行理解和推理的过程(缺乏高层语义知识引导)
(4)现有数据集 的质量还有待提升, 大量实际存在的小目标、模糊目标没有标注出来, 限制了现有算法潜力。
(5)旋转框更紧凑,但是相对于水平框精度比较低,定位不准确。
(6)针对遥感图像数据规模较大的问题, 现有方 法的处理速度较慢。
5.2 未来趋势
(1)采用基于图像整体进行感兴趣区域提取的方式来替代分块 处理方式, 可以快速滤除大部分背景区域, 从而避免计算冗余, 提高算法效率。
(2)加强小目标、 密集目标、模糊目标等较难检测目标的特征表示,降低背景干扰。
(3)引入知识和推理模块 (例 如知识图谱、图卷积等) 来辅助进行目标检测。
(4)采用弱监督学习、半监督学习、迁移学习等来解决标注的质量的问题
(5)遥感图像目标检测中旋转框具有更加精细的定位能力, 代替水平框进行检测是大势所趋,进一步提高定位的能力。
(6)轻量化网络的结构更具有重要意义与价值。网络架构搜索(NAS)也具有潜力。
留言